4 Jun 2024
Brief Overview
This article offers an in-depth exploration of Lockout Tagout (LOTO), a critical safety procedure designed to control hazardous energy during equipment maintenance and repair. We will cover the fundamentals of LOTO, provide real-world statistics and case studies, highlight key takeaways, identify common mistakes, introduce OSHEPRO, and share additional resources. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of the significance of LOTO and how to implement it effectively in your workplace.
OSHA Lockout Tagout Standard
The OSHA LOTO standard is generally applicable to any activity where unexpected equipment startup or energisation could harm employees. However, there are specific exceptions, such as construction, agriculture, maritime operations, oil and gas well drilling, and certain electrical work.
Importance of Lockout Tagout
One of the most common and dangerous workplace hazards is the accidental release of hazardous energy. This can lead to severe injuries or fatalities if proper safety procedures are not followed. Implementing LOTO procedures effectively reduces the risk of accidents, extends the lifespan of equipment, and minimizes the need for costly repairs. By isolating machinery and tagging it appropriately, LOTO ensures a safer working environment for all employees.
Common OSHA Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) Violations in 2023-2024
Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) procedures are critical for controlling hazardous energy. However, violations remain prevalent, leading to significant penalties across various industries.
Key Statistics (October 2022 - September 2023)
Total Citations: 2,532
Total Penalties: $20,876,780
Breakdown by Industry
- Manufacturing
Citations: 1,886
Penalties: $17,255,689 - Wholesale Trade
Citations: 159
Penalties: $884,658 - Administrative and Support Services
Citations: 92
Penalties: $834,833 - Other Services
Citations: 65
Penalties: $335,529 - Retail Trade
Citations: 46
Penalties: $207,726
Reference: Lockout/Tagout Standard
What exactly is Lockout Tagout?
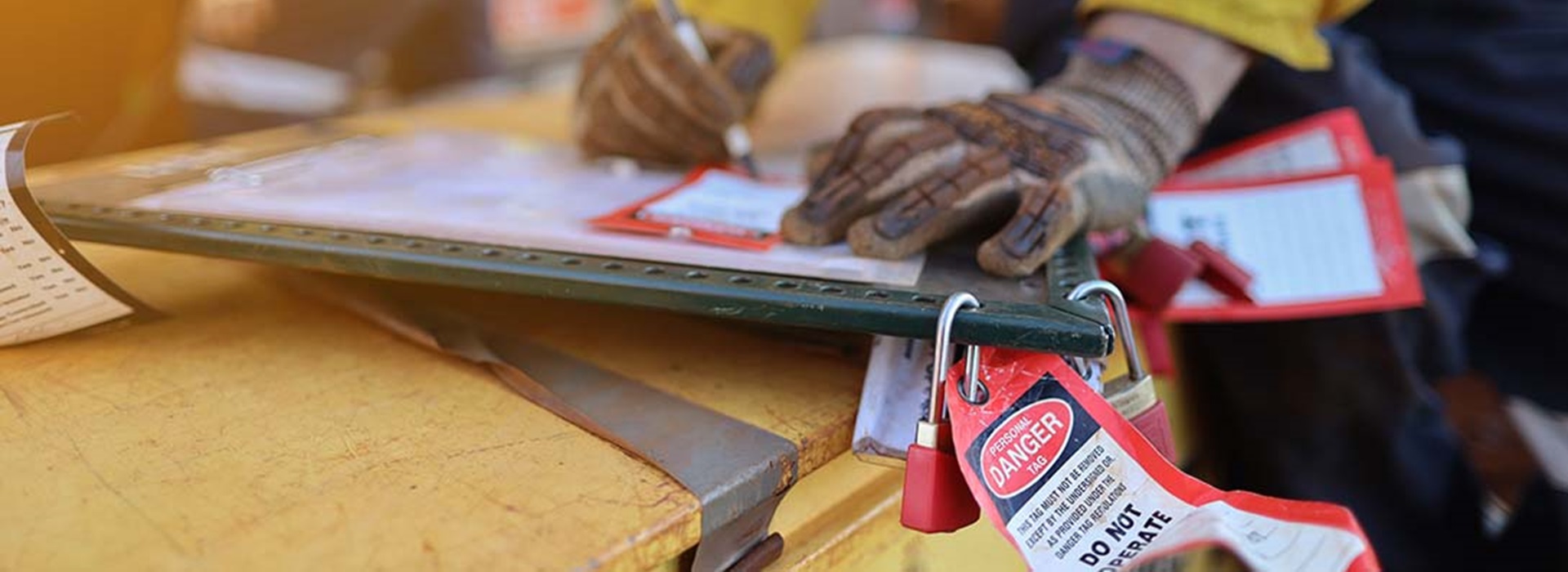
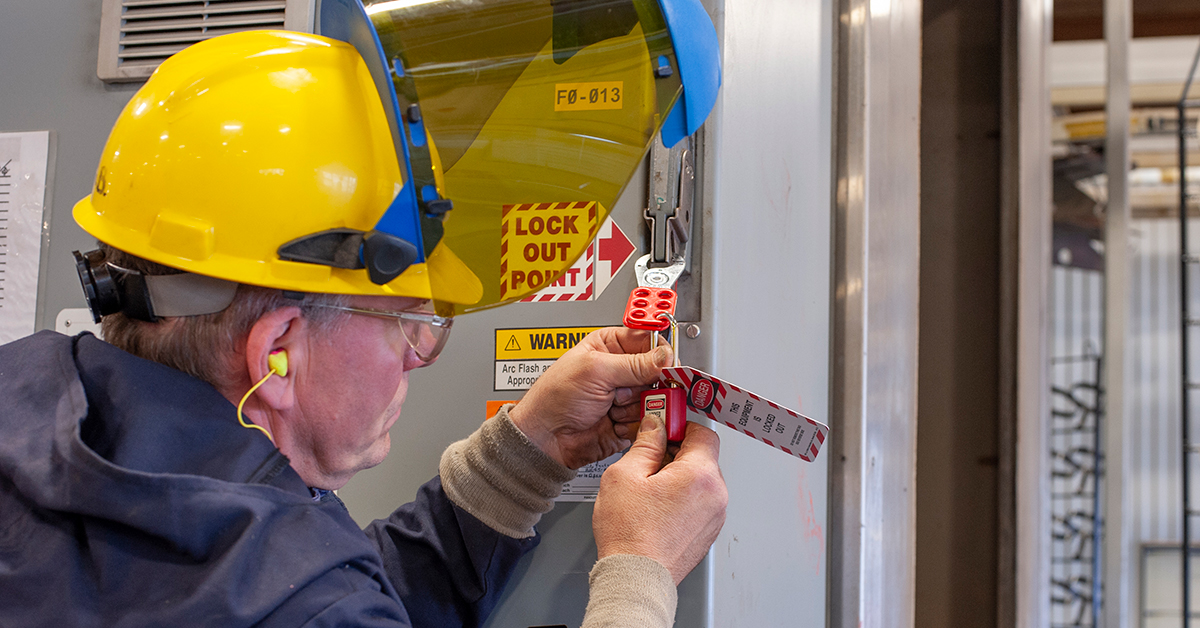
Lockout Tagout (LOTO) is a critical safety procedure designed to prevent the unintentional release of hazardous energy during the maintenance or repair of machinery and equipment. This procedure involves using lockout devices, such as padlocks, to physically secure energy-isolating devices and prevent equipment operation. Tagout devices, like warning tags, are then used to inform employees that the equipment should not be operated.
Establishing a Lockout Tagout Program
To be OSHA-compliant, a Lockout Tagout (LOTO) program must include:
- Lockout Tagout Procedures: Detailed equipment-specific procedures outlining the scope, purpose, and methods for energy isolation.
- Lockout Tagout Inspections: Regular inspections to verify proper application of LOTO procedures and identify potential issues.
- Lockout Tagout Training: Training for authorized, affected, and other employees to ensure understanding and compliance with LOTO procedures.
Understanding Lockout vs. Tagout
The primary difference between lockout and tagout lies in the devices used:
- Lockout Devices: These physically prevent the operation of equipment by securing energy-isolating devices, acting as the first line of defense.
- Tagout Devices: These serve as the second layer of protection by providing a visual warning that the equipment is under maintenance and should not be operated.
Lockout Tagout Devices
Employers must provide LOTO devices that are durable, standardized, substantial, and identifiable. These devices include:
- Energy Isolating Devices: Used to ensure secure isolation of energy sources.
- Electrical Lockout Devices: Secure electrical power in the "off" position.
- Multi-purpose Cable Lockout Devices: Lock out multiple energy isolation points.
- Valve Lockout Devices: Physically prevent the operation of valves.
- Lockout Devices: Hold energy-isolating devices in a safe position, preventing energization.
- Padlocks: Issued by the employer, standardized, and distinguishable for lockout purposes.
- Tagout Devices: Provide prominent warnings that equipment should not be operated.
- Tags: Act as warnings and contain information on the lockout condition, including the name of the person responsible.
- LOTO Box: Used for group lockout situations where multiple isolation points need securing.
Lockout Tagout Procedure
A comprehensive LOTO procedure involves seven steps:
- Preparation: Identify equipment and energy sources, recognizing potential hazards.
- Notification: Inform affected personnel about the shutdown, including details on equipment, reasons, and duration.
- Shutdown: Follow established shutdown procedures to ensure all running parts stop.
- Isolation: Remove the equipment from energy sources.
- Dissipation: Eliminate any residual energy.
- Lockout/Tagout: Secure equipment with lockout devices and attach tags with relevant information.
Isolation Verification: Re-check all steps and test equipment controls to confirm isolation.
Promoting LOTO Safety
To build a robust LOTO program, safety supervisors should:
1. Clearly Define and Communicate the LOTO Program
Ensure that all employees understand the LOTO program. The authority to write LOTO procedures should be extended to equipment operators /managers. This delegation allows safety managers, who may be occupied with various responsibilities, to focus on their other duties while empowering equipment operators and managers with a sense of ownership and responsibility. Once drafted, these procedures are reviewed by the safety manager for the final approval. OSHEPRO, an employee-owned EHS Management System, facilitates this process by providing an authority-based hierarchy to employees to develop LOCO procedures and to EHS leaders to authorize them. This sophisticated process streamlines the LOTO procedure writing and authorizing.
2. Perform Annual LOTO Audits
Conduct annual audits to comprehensively evaluate the facility’s LOTO program. Annual audits help identify potential gaps and areas for improvement, ensuring ongoing compliance and safety enhancements.
By implementing these steps and leveraging the capabilities of OSHEPRO, organizations can cultivate a safer working environment and maintain compliance with LOTO standards.
Additional Resources
For more detailed information, visit the official OSHA website: https://www.osha.gov/control-hazardous-energy













.png)



.png)


.png)




.jpg)